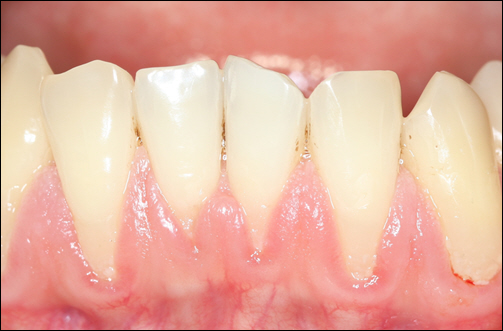
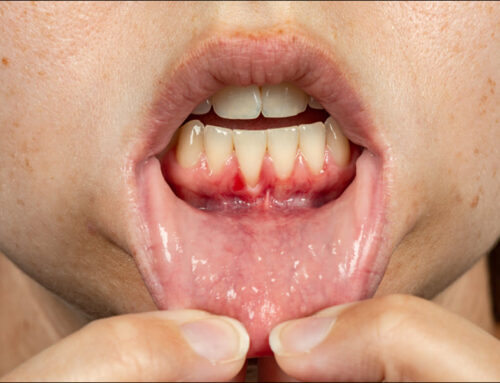
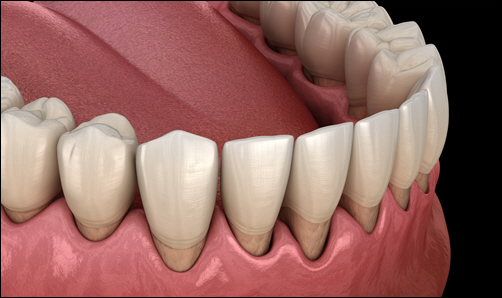
Gum recession, a condition where the gums pull back from the teeth, exposes more of the tooth’s surface and sometimes even its roots. Left untreated, periodontal issues with receding gums can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, decay, and eventually tooth loss. By identifying the early signs of recession and taking steps to correct it, you protect your teeth and preserve your smile. Here’s how to recognize it and what treatments are available to stop it in its tracks.
Causes
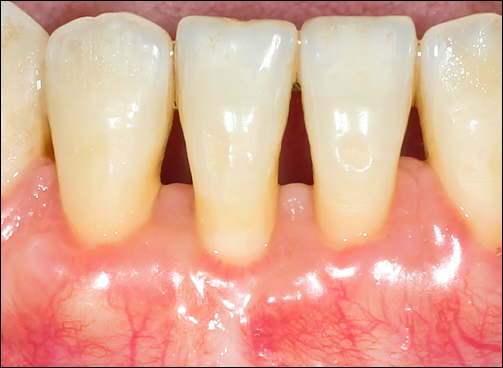 Gum recession can develop for several reasons, and understanding the cause helps you prevent further damage. Some common causes include:
Gum recession can develop for several reasons, and understanding the cause helps you prevent further damage. Some common causes include:
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard, especially with a hard-bristled toothbrush, wears away the enamel and irritates the gum tissue, causing it to recede over time. A gentle technique with a soft-bristled brush is essential for gum health.
- Gum Disease: Periodontal disease, caused by plaque buildup, inflames and weakens gum tissue, leading to recession. Untreated gum disease can progress, breaking down the bone and tissue that support your teeth.
- Genetics: Some people are more prone to recession due to their genetic makeup, even with good oral care practices.
- Misaligned Teeth: Teeth that are out of alignment can place extra pressure on the gums, causing them to wear down over time. Orthodontic treatment can help balance the bite and reduce recession.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco affects blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to infection and recession.
Recognizing the Signs
 Catching gum recession early is key. Signs to watch for include:
Catching gum recession early is key. Signs to watch for include:
- Sensitive Teeth: Exposed tooth roots are more sensitive to temperature changes and certain foods. If you notice increased sensitivity, especially near the gumline, it may indicate recession.
- Visible Tooth Roots: When gums recede, you may start to see more of your tooth’s surface or even the root itself.
- Longer-Looking Teeth: Teeth may appear longer as the gums pull back, exposing more of the tooth structure.
- Loose Teeth: Advanced gum recession weakens the support for your teeth, sometimes causing them to feel loose.
If you notice any of these signs, consult your dentist. Early intervention can prevent recession from worsening.
Correcting Gum Recession
Dentists offer several treatment options to stop and even reverse it, depending on its severity:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline, allowing the gums to reattach to the tooth surface. Scaling and root planing can be highly effective for early-stage recession caused by gum disease.
- Gum Graft Surgery: For more severe cases, your dentist may recommend gum grafting, where tissue is taken from another part of the mouth and attached to the receding area. This covers exposed roots, reduces sensitivity, and helps prevent further recession.
- Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST): This minimally invasive procedure uses small pinholes to reposition gum tissue over receded areas without the need for sutures. PST reduces recovery time and provides natural-looking results.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Misaligned teeth contribute to recession, so orthodontic treatment, such as braces or clear aligners, may be recommended to correct your bite and reduce gum stress.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting gentler brushing techniques, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, and quitting tobacco can all slow or stop gum recession.
Protecting Your Gums for the Long Term
Regular dental check-ups are essential to monitor gum health and catch early signs of recession. With early identification and proper care, you can preserve your gums, protect your teeth, and avoid the risks associated with untreated recession. By addressing gum recession promptly, you take the first step toward a healthier smile and ensure that your teeth stay strong and secure for years to come.