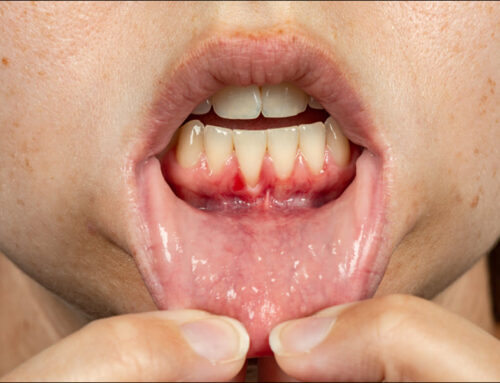
Gum pain can be a distressing and uncomfortable experience, often affecting your ability to eat, speak, and enjoy daily activities. While it can have several causes, the good news is that many of them are manageable and treatable with proper care. Understanding the potential causes of painful gums and exploring effective solutions can help you find relief and maintain optimal oral health.
Common Causes of Gum Pain
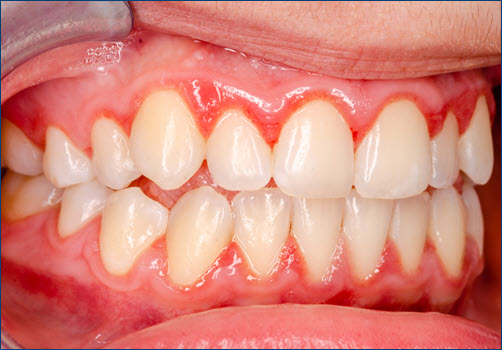 Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease, characterized by inflamed, red, and swollen gums. It is often caused by plaque buildup along the gum line due to poor oral hygiene. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe periodontal disease, leading to gum recession and tooth loss.
Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease, characterized by inflamed, red, and swollen gums. It is often caused by plaque buildup along the gum line due to poor oral hygiene. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe periodontal disease, leading to gum recession and tooth loss.- Periodontal Disease: Also known as periodontitis, this is a more advanced form of gum disease that affects the gums and the supporting structures of the teeth. It can cause severe gum pain, receding gums, and even tooth loss if not treated promptly.
- Mouth Ulcers: Canker sores or other types of mouth ulcers can develop on the gums, causing localized pain and discomfort. These sores are usually small, shallow lesions that can be triggered by stress, injury, or certain foods.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to gum pain. For example, oral thrush, a yeast infection, can cause white patches and soreness on the gums.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can increase gum sensitivity and lead to pain and swelling.
- Tooth Abscess: An untreated cavity or injury can lead to an abscess, which is a pocket of pus that forms in the tooth or gum. This can cause severe pain and swelling in the gums.
- Improper Dental Appliances: Ill-fitting dentures, braces, or retainers can irritate the gums and cause soreness and pain.
Solutions for Gum Pain
- Improve Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, and be gentle to avoid irritating the gums further.
- Rinse with Salt Water: A warm saltwater rinse can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the mouth. Mix one teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and swish it around your mouth for 30 seconds before spitting it out.
- Use a Medicated Mouthwash: Antibacterial mouthwashes can help reduce plaque and prevent gum disease. Look for mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine or other antibacterial agents.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the mouth moist and washes away food particles and bacteria.
- Avoid Irritating Foods: Spicy, acidic, or crunchy foods can aggravate gum pain. Opt for softer, milder foods until the pain subsides.
- Apply a Cold Compress: A cold compress can help numb the area and reduce swelling. Apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the outside of your cheek for 15 minutes.
- Visit Your Dentist: If gum pain persists or worsens, it’s essential to consult a dentist. They can diagnose the underlying cause of the pain and recommend appropriate treatment, such as scaling and root planing for gum disease or antibiotics for infections.
Painful gums can significantly impact your quality of life, but understanding its causes and solutions can help you find relief and maintain oral health. Practicing good oral hygiene, making dietary adjustments, and seeking professional dental care when needed are crucial steps in preventing and managing gum pain. Remember, addressing gum pain early can prevent more serious dental issues and ensure a healthy smile for years to come.